-
 Continue reading →: 3D Printed Brain!
Continue reading →: 3D Printed Brain!Hello dear readers. Whenever something incredible happens in the world of neuroscience, you can be sure that I will cover it. And that is what today’s short post is about. Today I wanted to share one amazing breakthrough made in the field of neuroscience with you all. This breakthrough is…
-
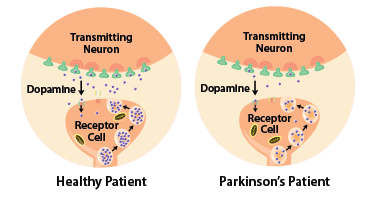 Continue reading →: Parkinson’s Disease
Continue reading →: Parkinson’s DiseaseParkinson’s disease, (PD) is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder. This disorder primarily affects the motor system, but also can impact behavior and sensory systems. In late stages, Parkinson’s can lead to Parkinson’s disease dementia. Cause of Parkinson’s The cause of Parkinson’s is the increase of neuron death in the substantia nigra. The substantia…
-
 Continue reading →: Alzheimer’s Disease
Continue reading →: Alzheimer’s DiseaseAlzheimer’s (also known as AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that results in memory loss and is responsible for 60% of dementia cases. 10.5% of people aged 65+ have Alzheimer’s. Although the cause is relatively unknown, there are several symptoms that we can look out for to identify symptoms. Symptoms of Alzheimer’s:…
-
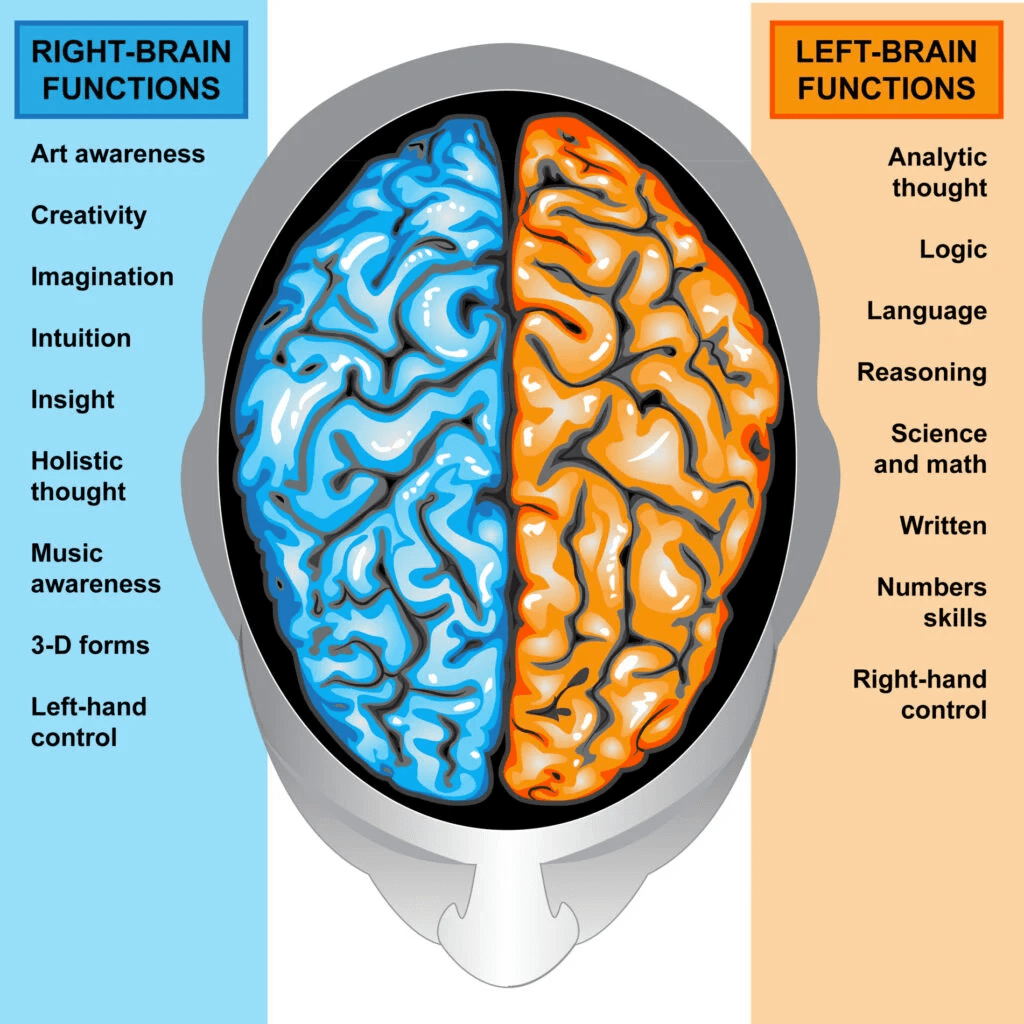 Continue reading →: Lateralization
Continue reading →: LateralizationWe know that the brain has two hemispheres, the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. We also know that both these hemispheres have the same four lobes. Yet, it has been proven that each hemisphere is better at certain functions. This tendency of the brain is known as lateralization. Division…
-
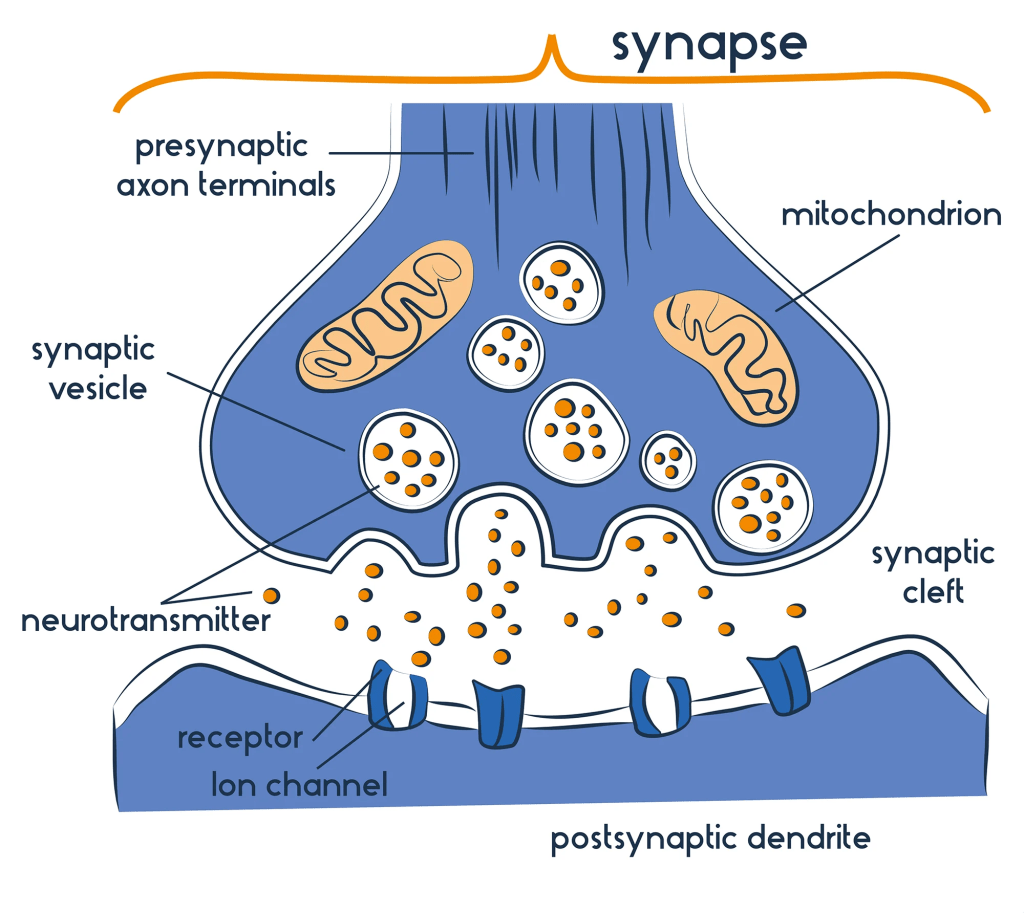 Continue reading →: Neurotransmitters
Continue reading →: NeurotransmittersNeurons communicate with two types of signals; electrical and chemical. Neurotransmitters are the chemical signals the send. Neurotransmitters are extremely vital for intra-neuron communication as well as communication with other parts of the body. The Science Behind Neurotransmitters First of all, how do neurotransmitters work? Well on a basic level,…
-
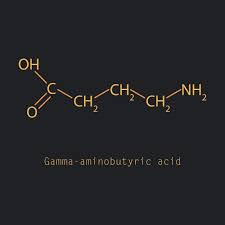 Continue reading →: Neuroplasticity and GABA
Continue reading →: Neuroplasticity and GABAIn the last few years, the word “neuroplasticity” has gained a lot of popularity. We hear it all the time in conversations related to learning, memory, and absorbing information. But what exactly is neuroplasticity, and why does it decrease as we grow? History of Neuroplasticity Over 100 years ago, William…
-
 Continue reading →: Peripheral and Central Nervous System
Continue reading →: Peripheral and Central Nervous SystemThe phrase central nervous system is thrown around a lot. But have you ever wondered why there was a need to clarify the “central” part of the nervous system? Well, believe it or not, there is another, separate nervous system, known as the periphery nervous system. Before diving into the…
-
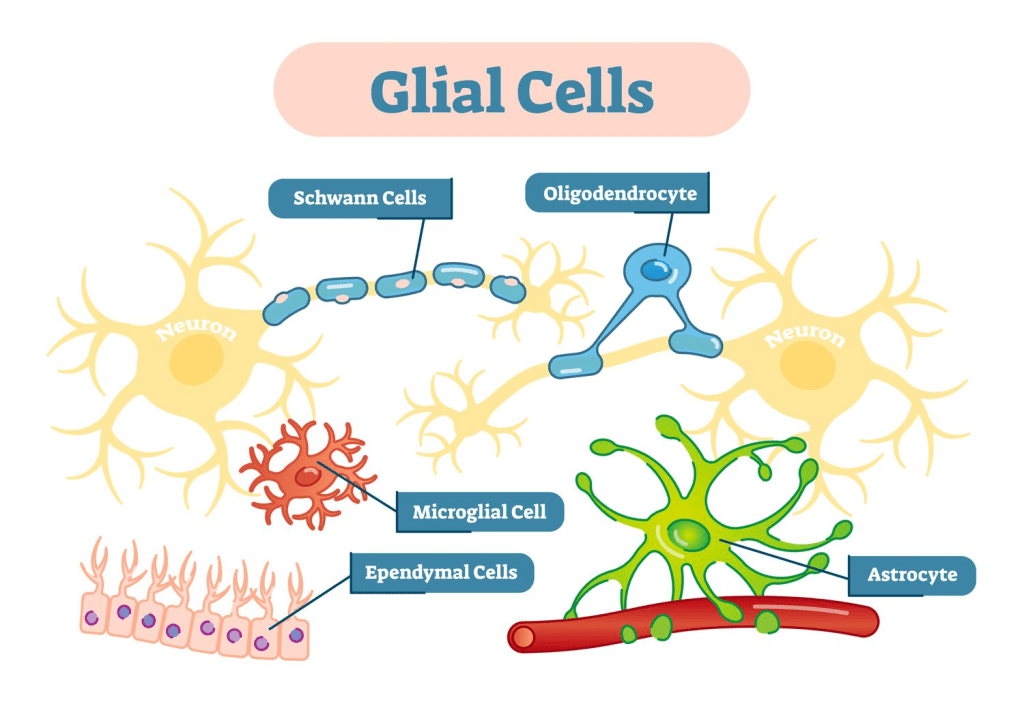 Continue reading →: Glial Cells: Function and Anatomy
Continue reading →: Glial Cells: Function and AnatomyGlial Cells. You’ve probably never heard of them. I know that until writing this article, I didn’t either. A quick google search shows that they work in correlation to neurons. But what exactly are glial cells? How do they work? And what is their purpose? Types of Glial Cells There…
-
 Continue reading →: Neurons: Functions & Anatomy
Continue reading →: Neurons: Functions & AnatomyHow do neurons work? We know that they allow us to think, reason, and a bunch of really cool stuff. We also know that we have 100 billion neurons in our brain. But still, how do neurons functions? Functions of a Neuron A neuron has three different basic functions: These…
-
 Continue reading →: Emotions, Memory, Intuition, and Chess?
Continue reading →: Emotions, Memory, Intuition, and Chess?So what is intuition? We all have felt it before, that “gut” feeling in our stomach, warning us. But what exactly is it. The more you think about it, the harder it becomes to define. Neuroscientists have defined it as the results of memories, emotions, and unconscious cognition. So we…
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.